This data report presents the findings of a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis conducted to assess the financial implications and potential returns on investment associated with radon mitigation in commercial buildings. The analysis evaluates the costs and benefits of implementing radon mitigation measures, including installation expenses, health benefits, productivity gains, regulatory compliance, and property value preservation. The report aims to provide stakeholders with valuable insights to support informed decision-making regarding commercial radon testing.
- Cost Analysis:
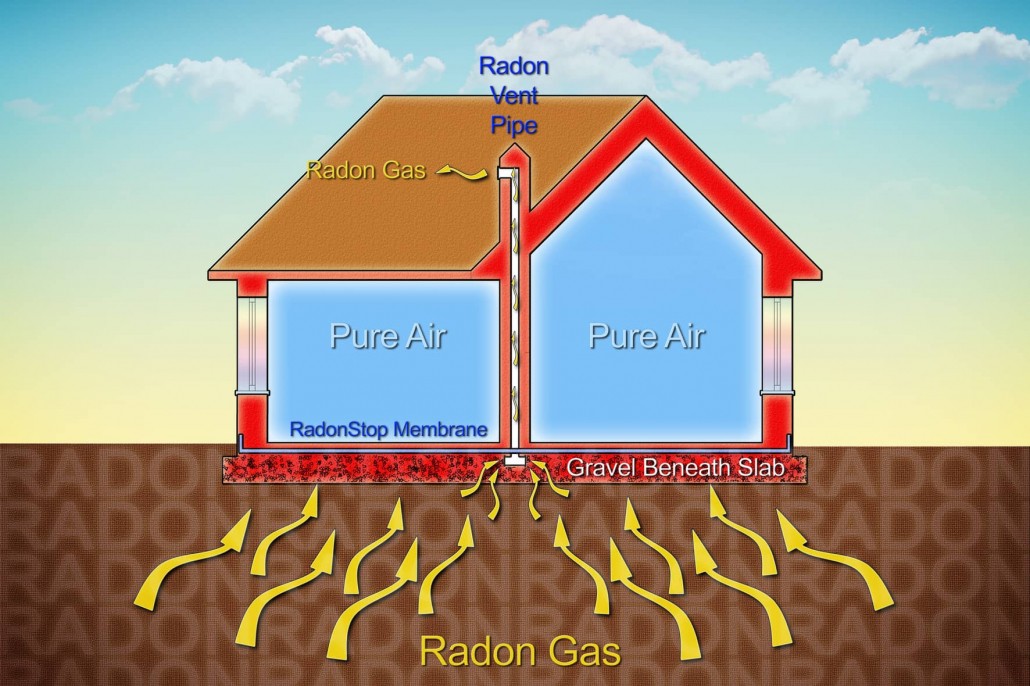
Mitigation System Installation: The estimated cost of installing a radon mitigation system in a commercial building range from $2,000 to $5,000, depending on the size and complexity of the building.
Initial Testing: Initial radon testing costs approximately $150 to $300 per test, including laboratory analysis fees and professional inspection services.
Ongoing Monitoring: Ongoing radon monitoring and testing incur annual costs of approximately $100 to $200 per test, including equipment rental or purchase and professional services.
Maintenance and Repairs: Maintenance and repair costs for radon mitigation systems vary but typically range from $100 to $500 per year, including routine inspections, filter replacements, and repairs as needed.

- Benefit Analysis:
Health Benefits: Radon mitigation can significantly reduce the risk of lung cancer and other respiratory illnesses associated with radon exposure, resulting in improved public health outcomes and potential healthcare cost savings.
Productivity Gains: Improved indoor air quality resulting from radon mitigation measures can lead to productivity gains through reduced absenteeism, increased employee morale, and enhanced workplace satisfaction.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with radon-related regulations and standards mitigates the risk of legal liabilities and fines, ensuring the commercial building meets health and safety requirements.
Property Value Preservation: Radon mitigation enhances the long-term value of the commercial property by addressing potential health hazards, improving marketability, and attracting tenants or buyers concerned about indoor air quality.
- Financial Metrics:
Net Present Value (NPV): The NPV of radon mitigation measures is calculated by subtracting the present value of costs from the present value of benefits over the expected lifespan of the mitigation system, using a discount rate of X%. A positive NPV indicates a favorable financial outcome.
Return on Investment (ROI): The ROI of radon mitigation is calculated by dividing the net benefits (total benefits minus total costs) by the total costs of mitigation, expressed as a percentage. A higher ROI signifies greater financial efficiency and effectiveness of the mitigation strategy.
Conclusion:
The data report highlights the importance of conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis to assess the financial viability and potential benefits of commercial radon testing. By weighing the costs against the benefits and considering key assumptions and uncertainties, stakeholders can make informed decisions to protect occupants’ health and safety while maximizing financial returns on investment in radon mitigation measures.



